What are the electrical losses in a transformer? What are the ways to reduce them?
Power losses are generally when the input power is not equivalent to the power output in a transformer. As the transformer is a static electrical device with no moving parts so there is only electrical losses and no mechanical losses. The different types of losses in a transformer are:
➤ Iron loss: also known as the core loss. This is constant and has two types: hysteresis and the eddy current loss.
✜ Eddy current loss: Gaps or empty spaces in a transformer core generates eddy current that flows in the opposite direction, and opposes the flow of the current. It reduces the efficiency of the alternating current.✜ Hysteresis loss: when the alternating current flows through the ferromagnetic core of the transformer it results in a rapid magnetization and demagnetization of the core. That creates a forward and reverse magnetic flux which eventually increases the temperature and causes energy loss.
➤ Copper/ ohmic loss: when the electric current flows through the wire, it faces some resistance. The resistance faced by the electric current in the copper winding of the transformer is called copper loss or ohmic loss. This is a variable loss that increases or decreases as the load on the transformer change respectively.
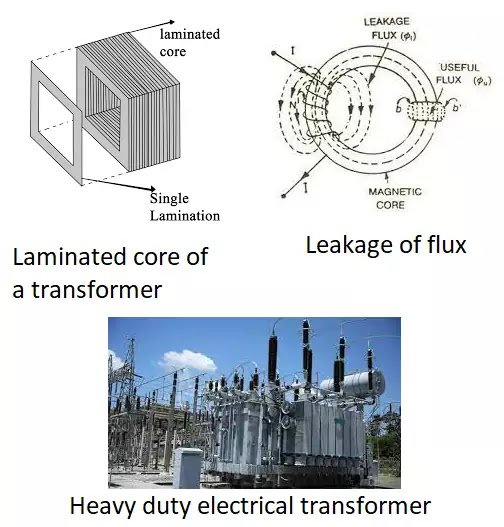
➤ Leakage of flux: the two windings in a transformer core are linked through the magnetic flux. In the process, some flux escapes out that develops an energy loss in the transformer.
The ways to reduce these electrical losses are:
- The core of an electrical transformer is made of laminated soft iron plates to reduce the empty spaces in between that develop eddy current. This helps to reduce the eddy current loss and also to reduce the leakage of flux in a transformer.
- Hysteresis loss can be reduced by replacing the soft iron core with a silicon steel core.
- Copper loss can be reduced by using wires with a large cross-sectional area in the manufacturing of those coils.
Tags:
Physics